In an era marked by climate change, soil degradation, and rapidly growing populations, ensuring food security has become a critical global challenge. Traditional agricultural practices are facing increasing limitations due to dwindling arable land, unpredictable weather patterns, and the depletion of natural resources. In response to these challenges, innovative solutions such as hydroponics have emerged as promising alternatives, offering sustainable and efficient methods of food production. This article explores the concept of hydroponics, its advantages in enhancing food security, and its role in shaping the future of agriculture.

Understanding Hydroponics
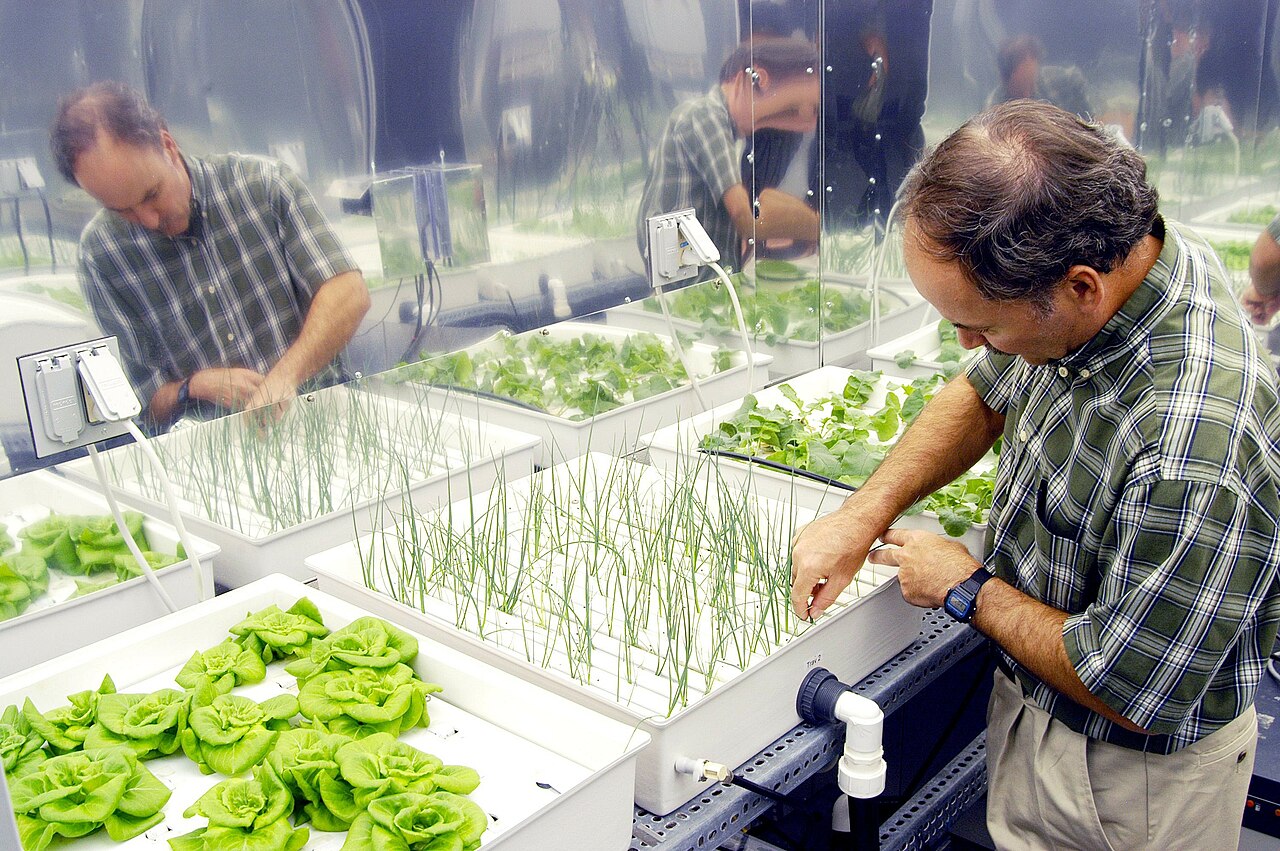
Hydroponics is a soilless farming technique that involves cultivating plants in nutrient-rich water solutions instead of soil. This method relies on various systems such as nutrient film technique (NFT), deep water culture (DWC), and aeroponics to deliver essential nutrients directly to the plant roots. By providing plants with precisely controlled environments, hydroponic systems optimize growth conditions, resulting in faster growth rates and higher yields compared to traditional farming methods.
Advantages of Hydroponics for Food Security
- Maximized Space Utilization: One of the primary advantages of hydroponics is its ability to maximize space utilization. Unlike conventional farming, which relies on vast expanses of arable land, hydroponic systems can be implemented in diverse settings, including urban areas and arid regions. Vertical hydroponic setups, for example, allow growers to stack multiple layers of plants vertically, significantly increasing production capacity without the need for additional land.
- Water Efficiency: Hydroponic systems are highly water-efficient, utilizing up to 90% less water compared to traditional soil-based agriculture. Through recirculation and efficient nutrient delivery mechanisms, hydroponics minimizes water wastage while ensuring optimal hydration for plants. This feature is particularly advantageous in regions facing water scarcity or drought conditions, where traditional farming practices may be unsustainable.
- Nutrient Optimization: In hydroponic systems, nutrients are directly delivered to plant roots in precise concentrations, ensuring optimal uptake and utilization. This level of nutrient control minimizes the risk of nutrient deficiencies or imbalances, resulting in healthier plants and higher yields. Additionally, hydroponic solutions can be tailored to specific crop requirements, allowing growers to optimize nutrient formulations for different plant varieties and growth stages.
- Year-Round Production: Hydroponic farming enables year-round production independent of seasonal constraints. By controlling environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and light cycles, growers can create ideal growing conditions regardless of external weather conditions. This continuous production cycle enhances food security by reducing reliance on seasonal harvests and minimizing supply chain disruptions caused by adverse weather events.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: Compared to traditional agriculture, hydroponics has a significantly lower environmental impact. By eliminating the need for soil tillage and minimizing pesticide and fertilizer runoff, hydroponic systems mitigate soil erosion, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the controlled indoor environments of hydroponic farms reduce the risk of pest infestations and disease outbreaks, decreasing the reliance on chemical interventions.
- Localization of Food Production: Hydroponic farming promotes the localization of food production, reducing dependence on long-distance transportation and distribution networks. By establishing hydroponic facilities closer to urban centers and consumer markets, growers can minimize carbon emissions associated with food transportation while ensuring fresher and more nutritious produce for consumers.
The Role of Hydroponics in Enhancing Food Security
In the face of growing global challenges such as climate change, population growth, and resource scarcity, hydroponics offers a sustainable and scalable solution to enhance food security. By leveraging advanced technologies and innovative farming practices, hydroponic systems empower growers to produce more food using fewer resources, thereby increasing agricultural resilience and mitigating the impacts of environmental stressors.
Moreover, hydroponic farming holds the potential to transform food production in both developed and developing countries. In urban areas, where land availability is limited and demand for fresh produce is high, hydroponic vertical farms can utilize underutilized spaces such as rooftops, warehouses, and vacant lots to establish productive growing environments. Similarly, in rural communities facing agricultural challenges such as soil degradation and water scarcity, hydroponics can offer an alternative approach to traditional farming, enabling farmers to diversify their crops and improve livelihoods.

Tomato cultivation in hydroponics technique.
Hydroponics for Climate-Resilient Agriculture
Climate change poses unprecedented challenges to traditional farming practices, including erratic weather patterns, prolonged droughts, and extreme temperatures. Hydroponic systems offer a climate-resilient alternative by providing controlled environments where temperature, humidity, and other variables can be optimized for plant growth. This resilience ensures consistent yields despite external climatic variations, thereby mitigating the risks associated with climate-induced crop failures and enhancing overall food security.
Hydroponics for Resource-Efficient Farming
In a world grappling with dwindling natural resources, hydroponics emerges as a beacon of resource efficiency in agriculture. By eliminating the need for soil, hydroponic systems minimize land requirements, making them suitable for urban and peri-urban areas where arable land is scarce. Moreover, the precise delivery of nutrients directly to plant roots maximizes nutrient uptake, resulting in higher yields with minimal inputs. This resource-efficient approach not only conserves land and water but also reduces the reliance on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, thereby promoting sustainable food production practices.
Hydroponics for Rapid and Year-Round Production
Traditional farming practices are often limited by seasonal constraints, leading to cyclical patterns of abundance and scarcity in food production. Hydroponic farming disrupts this cycle by enabling rapid and year-round production of fresh produce. With hydroponics, growers can manipulate environmental factors such as light, temperature, and humidity to create optimal growing conditions regardless of the external season. This continuous production cycle ensures a steady and reliable food supply, thereby enhancing food security and reducing vulnerability to seasonal fluctuations in harvests.
Hydroponics for Urban Food Sovereignty
As urbanization accelerates worldwide, the need for locally produced food has become increasingly pressing. Hydroponic farming offers a viable solution to address this challenge by enabling food production within urban areas, closer to consumers. Vertical hydroponic systems, in particular, allow growers to maximize space utilization by stacking multiple growing layers vertically, making efficient use of limited urban real estate. By promoting urban agriculture and shortening the food supply chain, hydroponics enhances urban food sovereignty, empowering communities to meet their dietary needs locally and sustainably.
Hydroponics for Diverse Crop Cultivation
Hydroponic systems are versatile platforms that support the cultivation of a wide range of crops, including leafy greens, herbs, fruits, and even root vegetables. This versatility allows growers to diversify their crop portfolios and adapt to changing market demands and dietary preferences. Moreover, hydroponics enables the cultivation of crops in regions where traditional farming may be impractical or unfeasible due to soil infertility, salinity, or other environmental constraints. By expanding the range of cultivable crops, hydroponics enhances food security by increasing dietary diversity and reducing dependence on a few staple crops.
Hydroponics for Community Empowerment and Resilience
In addition to its agricultural benefits, hydroponics fosters community empowerment and resilience by providing opportunities for local entrepreneurship and self-sufficiency. Community-based hydroponic initiatives, such as school gardens, rooftop farms, and cooperative enterprises, empower individuals and communities to take control of their food production. By engaging in hydroponic farming, communities can build resilience against external shocks, such as economic downturns or disruptions in food supply chains. Moreover, hydroponic farming creates avenues for skill development, education, and social cohesion, strengthening the fabric of communities and enhancing their capacity to withstand adversity.

Use of Blockchain technology in Hydroponics
The convergence of hydroponics and blockchain technology heralds a new era in agriculture, marked by unprecedented efficiency, transparency, and sustainability. Hydroponics, with its soilless cultivation methods, optimizes resource usage and maximizes crop yields in controlled environments. Meanwhile, blockchain technology revolutionizes data management by providing a secure, decentralized ledger that records every transaction and activity along the hydroponic farming supply chain. This integration enables real-time tracking and traceability of produce, from seed to harvest to consumer, fostering trust and accountability in the agricultural ecosystem. Moreover, blockchain facilitates immutable product authentication, allowing consumers to verify the origin and quality of hydroponically grown produce, thereby combating food fraud and ensuring food safety. By leveraging blockchain’s data-sharing capabilities, hydroponic growers can access valuable insights and analytics, optimizing cultivation practices and driving innovation in sustainable agriculture. Together, hydroponics and blockchain technology offer a powerful synergy that promises to reshape the future of farming, promoting resilience, transparency, and environmental stewardship in food production.

Conclusion
In conclusion, hydroponics represents a paradigm shift in agricultural practices, offering a sustainable and efficient solution to enhance food security in the face of global challenges. By maximizing space utilization, optimizing resource efficiency, and reducing environmental impact, hydroponic farming has the potential to revolutionize the way we produce and consume food. As the world continues to grapple with the complexities of food security, embracing innovative approaches like hydroponics will be crucial in building a resilient and sustainable food system for future generations.
Related Articles:
- Urban Farming: Cultivating Sustainability in Cities
- The Future of Agriculture: Trends and Innovations
By incorporating hydroponics into agricultural practices, we can address food security challenges while fostering sustainability and resilience in our food systems.








Hello,
New club music, private server MP3/FLAC, Label, LIVESETS, Music Videos https://0daymusic.org
Available only on our secure FTP server,
Thanks for writing this article. This helped me alot. I hope this will be helpful for others.